Uganda and Rwanda are two East African countries with a shared history and a complex relationship. The two countries have been involved in a number of conflicts over the years, including the Uganda-Rwanda War of 1998-2001. Uganda Versus Rwanda: A Historical Rivalry In East Africa
Transition to main article topics
East Africa: Safaris - Chapter 4 - 2014 Yellow Book | Travelers' Health - Source wwwnc.cdc.gov
FAQ
Uganda and Rwanda, neighboring East African countries, have had a strained relationship for decades. This rivalry is rooted in historical grievances, cultural differences, and political disputes. To shed light on this complex issue, let's address some frequently asked questions:

Gorilla Trekking: Uganda Versus Rwanda, Which Is Better? – SafariBookings - Source www.safaribookings.com
Question 1: What are the historical roots of the Uganda-Rwanda rivalry?
The rivalry can be traced back to the colonial era, when both countries were under British rule. The British implemented policies that favored Uganda, creating resentment among Rwandans. Additionally, Rwanda accused Uganda of supporting rebel groups that sought to overthrow the Rwandan government.
Question 2: How have cultural differences contributed to the tension?
Uganda and Rwanda have distinct cultural traditions, leading to misunderstandings and mistrust. For instance, Uganda's emphasis on individualism contrasts with Rwanda's collectivist society. These differences have resulted in communication barriers and interpersonal conflicts.
Question 3: What are the main political disputes between the two countries?
Territorial disputes, border closures, and diplomatic conflicts have strained relations. Rwanda has accused Uganda of violating its territorial integrity by supporting rebel groups, while Uganda has accused Rwanda of interfering in its internal affairs.
Question 4: Have there been any attempts to resolve the rivalry?
Yes, there have been diplomatic efforts to improve relations, including regional summits and mediation by international organizations. However, these efforts have faced challenges due to ongoing mistrust and unresolved grievances.
Question 5: What are the potential consequences of the ongoing rivalry?
The rivalry has hindered regional integration, economic cooperation, and security in East Africa. It has also fueled tensions between the two peoples, creating an environment of mistrust and animosity.
Question 6: Is there hope for reconciliation between Uganda and Rwanda?
Reconciliation is possible but requires genuine political will, transparent dialogue, and a commitment to address historical grievances. Both countries must recognize the benefits of cooperation and overcome the legacy of mistrust.
The Uganda-Rwanda rivalry is a complex issue with historical, cultural, and political dimensions. Understanding the underlying factors is crucial for finding a path towards reconciliation and regional stability.
Tips
To gain insights on the historical rivalry between Uganda and Rwanda, consider exploring reputable sources and materials. A prime example is the article titled Uganda Versus Rwanda: A Historical Rivalry In East Africa, which offers a detailed examination of this complex relationship.
Tip 1: Understand the historical context:
Delve into the colonial era and post-independence dynamics that shaped the relationship between the two nations.
Tip 2: Examine political differences:
Analyze the contrasting political ideologies and leadership styles that have influenced the rivalry.
Tip 3: Consider economic factors:
Assess the competition for resources, trade disputes, and economic disparities that have contributed to tensions.
Tip 4: Explore regional dynamics:
Examine the involvement of neighboring countries and international organizations in shaping the relationship between Uganda and Rwanda.
Tip 5: Evaluate efforts for reconciliation:
Review attempts and initiatives aimed at resolving conflicts and fostering cooperation between the two countries.
By following these tips, you will gain a comprehensive perspective on the historical rivalry between Uganda and Rwanda, its causes, and potential steps towards reconciliation.
Uganda Versus Rwanda: A Historical Rivalry In East Africa
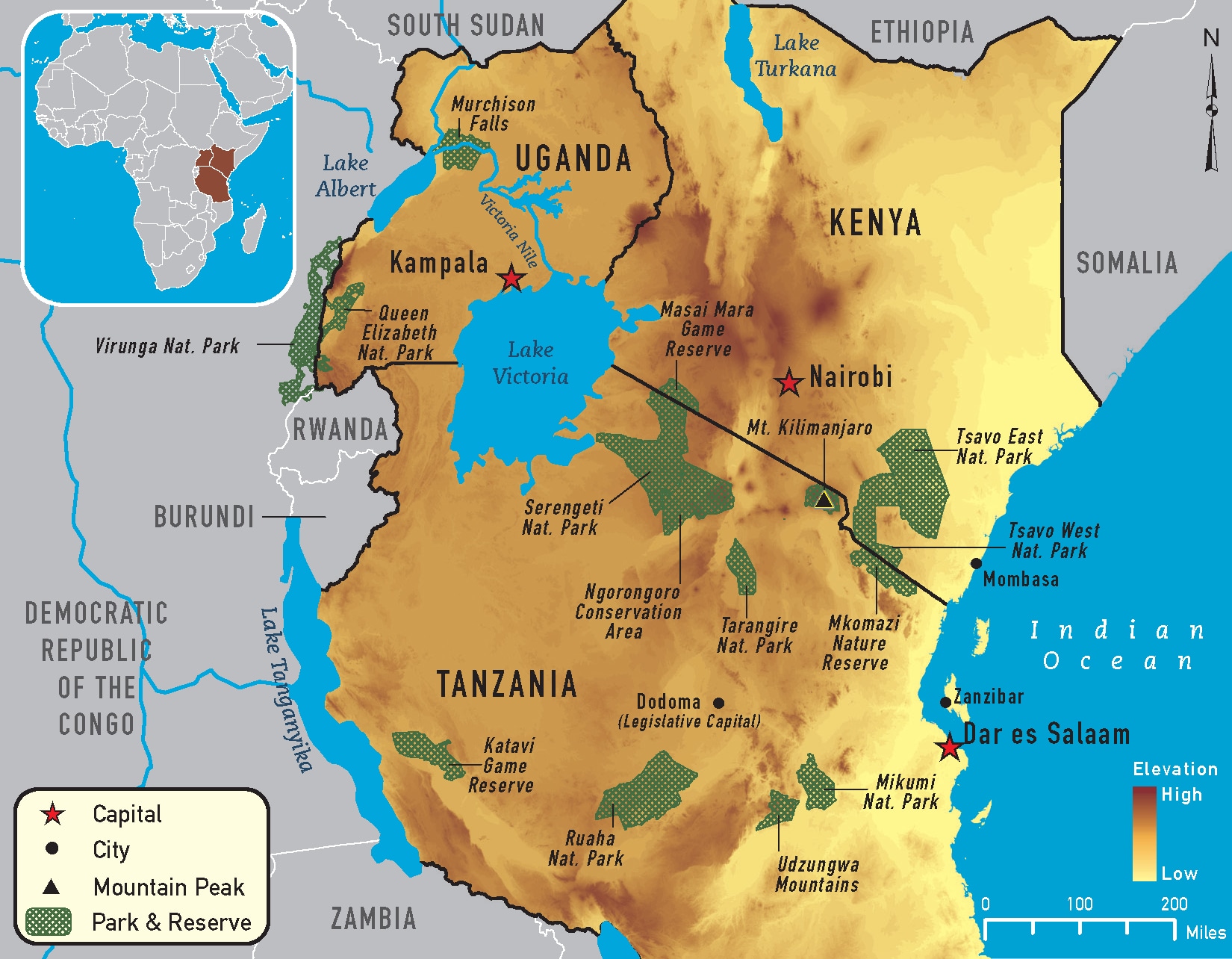
Uganda and Rwanda, located in the heart of East Africa, share a complex and often volatile relationship rooted in historical, political, and economic factors. The rivalry between these two nations has shaped the region's dynamics, with far-reaching consequences for their citizens and the broader East African community.
- Historical Antecedents: Colonial legacies, ethnic tensions, and border disputes have laid the groundwork for the rivalry.
- Political Ideologies: Differing political systems and ideologies have contributed to mistrust and conflict between the two countries.
- Economic Competition: Competition for resources, trade routes, and regional influence has fueled tensions.
- Cross-Border Conflicts: Armed conflicts along the shared border have further escalated the rivalry.
- Regional Dynamics: Uganda and Rwanda's rivalry has impacted regional stability and cooperation.
- Diplomatic Relations: Fluctuating diplomatic relations have exacerbated tensions and hindered reconciliation efforts.
The key aspects of the Uganda-Rwanda rivalry highlight the multifaceted nature of this conflict. Historical grievances, political differences, economic competition, and cross-border clashes have all played a role in shaping the strained relations between these two East African nations. Understanding these aspects is crucial for navigating the region's complex political landscape and fostering regional cooperation.

Combat Versus for Gaming Enthusiasts PNG | PNG All - Source www.pngall.com
Uganda Versus Rwanda: A Historical Rivalry In East Africa
The rivalry between Uganda and Rwanda is a complex and multifaceted issue with deep historical roots. The two countries have a long history of conflict and cooperation, and their relationship has been shaped by a number of factors, including ethnic tensions, economic competition, and political instability.
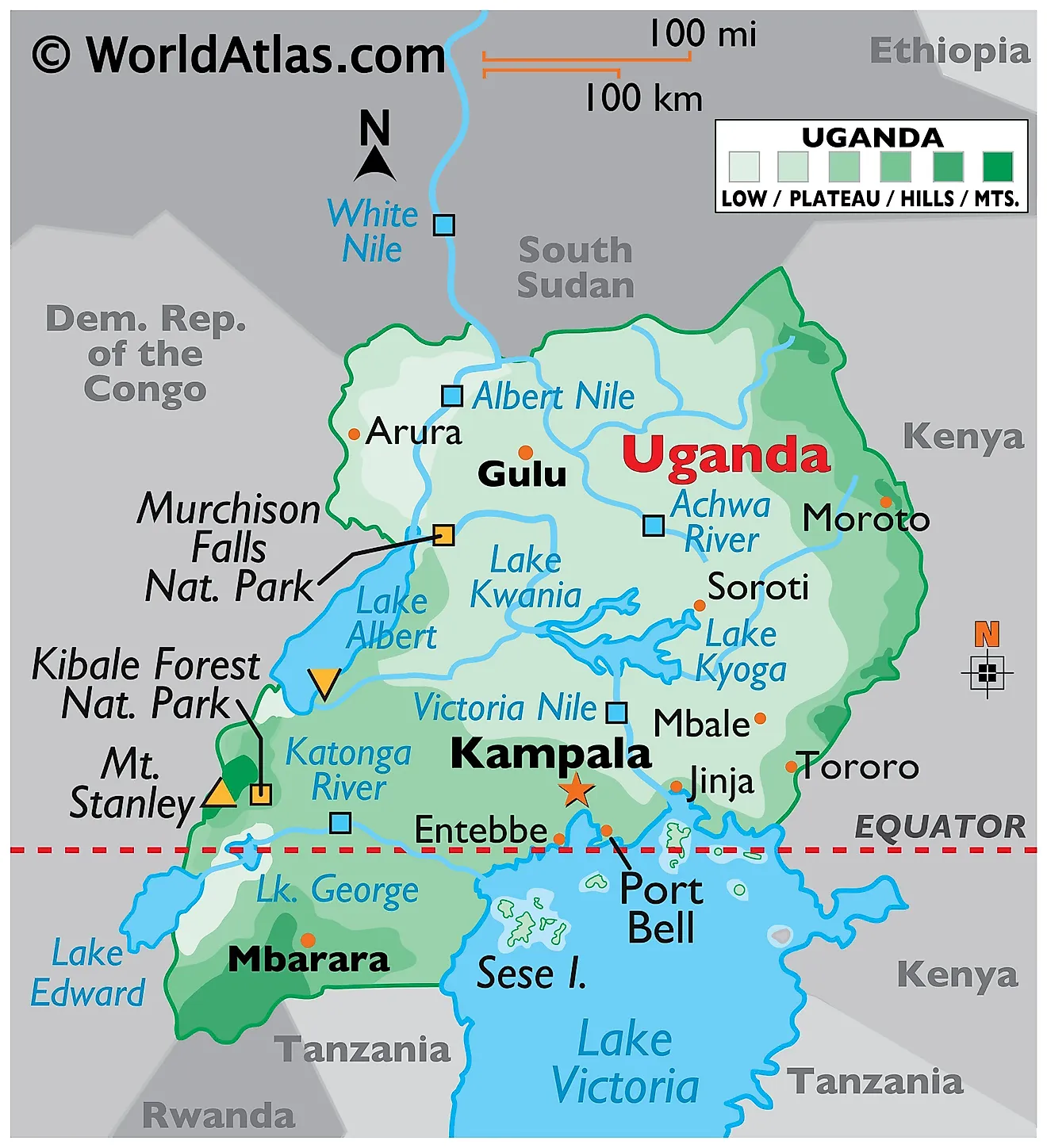
Mapas de Uganda - Atlas del Mundo - Source atlasdelmundo.com
One of the most significant factors in the Uganda-Rwanda rivalry is the issue of ethnicity. Uganda is home to a number of different ethnic groups, including the Baganda, the Banyarwanda, and the Bakonjo. Rwanda, on the other hand, is a much more ethnically homogeneous country, with the Tutsi and Hutu making up the vast majority of the population. This ethnic difference has been a source of tension between the two countries, and it has played a role in a number of conflicts, including the Rwandan Genocide of 1994.
Another factor that has contributed to the Uganda-Rwanda rivalry is economic competition. Uganda and Rwanda are both landlocked countries with limited natural resources. This has led to competition for scarce resources, such as land and water. In addition, the two countries have competing economic interests. Uganda is a major producer of coffee, while Rwanda is a major producer of tea. This competition has led to trade disputes and other economic tensions.
Finally, the Uganda-Rwanda rivalry has been shaped by political instability. Both countries have experienced periods of political turmoil, and this has led to changes in their relationship. For example, in the 1970s, Uganda was ruled by Idi Amin, a brutal dictator who expelled Rwandan refugees from Uganda. This led to a period of tension between the two countries. In the 1990s, Rwanda was ravaged by a genocide that killed over 800,000 people. This genocide had a profound impact on Uganda, and it led to a period of sympathy and support for Rwanda.
Conclusion
The rivalry between Uganda and Rwanda is a complex and multifaceted issue with deep historical roots. The two countries have a long history of conflict and cooperation, and their relationship has been shaped by a number of factors, including ethnic tensions, economic competition, and political instability.
The Uganda-Rwanda rivalry is a reminder of the challenges faced by African countries in the post-colonial era. These countries are struggling to build stable and prosperous societies, and they are often faced with challenges such as ethnic conflict, economic inequality, and political instability. The Uganda-Rwanda rivalry is a case study in these challenges, and it is a reminder of the importance of finding ways to resolve conflict and build cooperation.